In commercial lending, financial spreads are the foundation of every credit decision. They influence risk ratings, pricing, approval timelines, and portfolio health. Yet even experienced lending teams know that spreading errors are surprisingly easy to introduce, and difficult to catch once they move downstream.
Unlike consumer lending, commercial spreads involve multiple documents, varying formats, and borrower complexity. A single missed line item or misclassified value can distort cash flow analysis, debt service coverage, or leverage ratios. Over time, these small errors compound, slowing approvals, creating rework, and increasing risk exposure.
This blog breaks down the most common places errors show up in commercial spreads, why they happen, and what lenders can do to reduce them without adding friction to their workflows.
Key Insights at a Glance
- Most spreading errors originate during manual data extraction, not underwriting
- Inconsistent document formats are a major source of misclassification
- Multi-entity borrowers significantly increase error risk
- Spreadsheet-based workflows make errors harder to detect and correct
- Standardization and automation help reduce rework and improve accuracy
- Catching errors earlier leads to faster decisions and stronger portfolio oversight
Table of Contents
Why Spreading Errors Matter More Than Ever
Spreading errors don’t just affect individual deals. They ripple across operations.
Underwriters spend time validating numbers instead of evaluating risk. Credit committees lose confidence in financial outputs. Borrowers face delays due to rework and clarification requests. Portfolio reporting becomes less reliable over time.
In a competitive environment where speed and accuracy both matter, even small inefficiencies can turn into lost opportunities.

Where Errors Most Commonly Show Up in Commercial Spreads
1. Manual Data Entry and Re-Keying
Manual re-entry remains one of the biggest sources of error in commercial spreading. Analysts often extract numbers from PDFs, scanned statements, or tax forms and manually input them into spreadsheets or LOS templates.
Error rates for manual data entry tasks can be high: research shows that even skilled professionals are prone to mistakes such as transposed digits or misplaced decimals when entering data manually, and studies suggest error rates for manual entry can range from around 1% up to 4-5% depending on the volume and format of data handled. These seemingly small percentages become costly in high-volume operational environments like lending, where errors can cascade through spreads and distort key credit metrics.
Common issues include transposed digits, missed negative values, incorrect decimal placement, and line items copied into the wrong category. Even highly experienced analysts aren’t immune. When documents are long or poorly formatted, fatigue and repetition increase error risk.
2. Inconsistent Income Statement Classification
Income statements vary widely by borrower, accountant, and industry. Revenue, operating expenses, and non-recurring items are often labeled differently across statements.
Errors tend to show up when one-time expenses are treated as recurring, owner compensation is misclassified, EBITDA adjustments are applied inconsistently, or revenue categories are combined incorrectly. These classification issues can materially affect cash flow analysis and debt service calculations.
3. Balance Sheet Mapping Issues
Balance sheets introduce a different type of complexity. Assets, liabilities, and equity must align logically, but manual spreading often leads to mapping inconsistencies.
Short-term and long-term debt may be misaligned, current portions of long-term debt overlooked, or retained earnings misapplied year over year. When balance sheets don’t tie cleanly, analysts are forced to stop and reconcile manually, slowing the entire credit process.
4. Multi-Entity Borrower Complexity
Borrowers with multiple operating entities significantly increase spreading risk. Each entity may have its own income statement, balance sheet, and tax documentation.
Errors often appear when financials are reviewed in isolation, intercompany relationships are misunderstood, or debt obligations are double-counted or omitted. Without a standardized approach, multi-entity deals frequently require multiple revisions before reaching credit committee.
5. Spreadsheet Version Control and Rework
Spreadsheet-based workflows make it difficult to track changes over time. Multiple versions of the same file circulate across teams, increasing confusion.
Analysts may work from outdated numbers, corrections may appear in one version but not another, and audit visibility becomes limited. The more hands that touch a spread, the harder it becomes to ensure accuracy.
Subscribe to BeSmartee 's Digital Mortgage Blog to receive:
- Mortgage Industry Insights
- Security & Compliance Updates
- Q&A's Featuring Mortgage & Technology Experts
Why These Errors Are Hard to Catch
Most spreading errors don’t look obvious at first glance. They hide inside formulas, classifications, and assumptions. By the time inconsistencies surface, they’ve already slowed approvals or triggered rework.
The challenge isn’t lack of expertise. It’s process friction. Manual workflows make it harder to validate data quickly and consistently across teams.

Q&A: What Lenders Ask About Spreading Accuracy
Q: Aren’t these errors just part of the process?
A. Some level of review is always necessary, but repeated rework caused by manual entry and inconsistent classification is avoidable with better structure and tooling.
Q: Why do errors happen even with experienced analysts?
A. Because the issue isn’t skill. It’s volume, repetition, and unstructured data. Manual processes introduce risk regardless of experience level.
Q: How early should errors be addressed?
A. The earlier, the better. Catching issues during data extraction is far less costly than fixing them during underwriting or committee review.
Reducing Errors Requires Earlier Intervention
Many spreading errors don’t originate during underwriting. They begin much earlier, during document intake and data extraction, when borrower financials are first translated from PDFs and scanned files into spread-ready data.
When this early stage relies heavily on manual re-keying, inconsistencies and transcription errors are almost inevitable. Addressing error risk at the front of the workflow creates a stronger foundation for everything that follows.
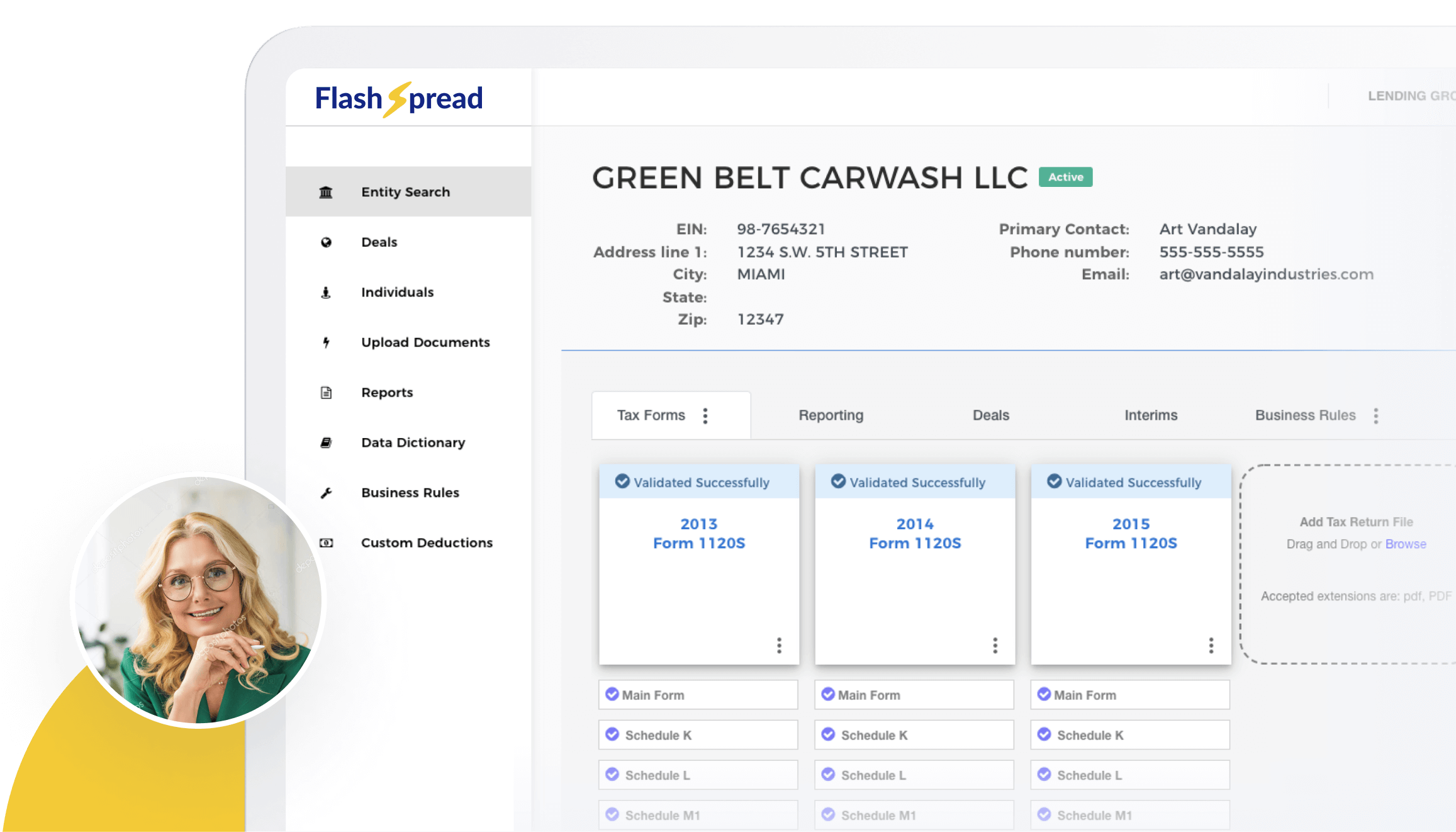
Where FlashSpread Fits Into Error Reduction
Many spreading errors don’t originate during underwriting. They start earlier, during document intake and data extraction, when financial data is first translated from PDFs, scans, and unstructured files into spread-ready information.
When this step relies on manual re-keying, errors such as misclassification, missed line items, or inconsistent mapping are difficult to avoid. Improving accuracy at this early stage creates a stronger foundation for every credit decision that follows.
FlashSpread is designed to address this exact challenge by applying advanced OCR and machine learning to the spreading process. Its AI-driven extraction engine reads and organizes financial data from structured, unstructured, and scanned documents, including tax returns, income statements, and balance sheets. By learning common document patterns and financial layouts, FlashSpread reduces reliance on manual re-keying and helps standardize how data enters the spreading workflow—supporting cleaner, more consistent analysis without replacing analyst judgment.
With this approach, lenders can:
- Minimize transcription and data entry errors during spreading
- Apply consistent data structure across income statements and balance sheets
- Reduce the need for manual re-input when borrowers submit multiple documents
- Surface inconsistencies earlier, before files reach underwriting or credit committee
- Shorten review cycles by working from cleaner, standardized financial data
By automating the most error-prone parts of spreading, FlashSpread helps teams spend less time reconciling numbers and more time evaluating risk. This is especially valuable for high-volume pipelines or complex borrower structures, where small errors can quickly multiply into larger delays.
Roundup
Spreading errors are one of the most common and costly sources of friction in commercial lending. They make slow decisions, increase rework, and introduce unnecessary risk across portfolios.
By understanding where errors most often appear and why they happen, lenders can take meaningful steps to reduce them. Standardization, early validation, and automation all play a role in creating cleaner spreads and more confident credit decisions.
Reducing errors isn’t about cutting corners. It’s about building processes that support accuracy, speed, and scale, without adding complexity.
If your team is spending too much time fixing spreads instead of evaluating deals, it may be time to rethink how financial data enters your workflow. Learn how FlashSpread helps lenders reduce errors and move from documents to decisions with greater confidence.